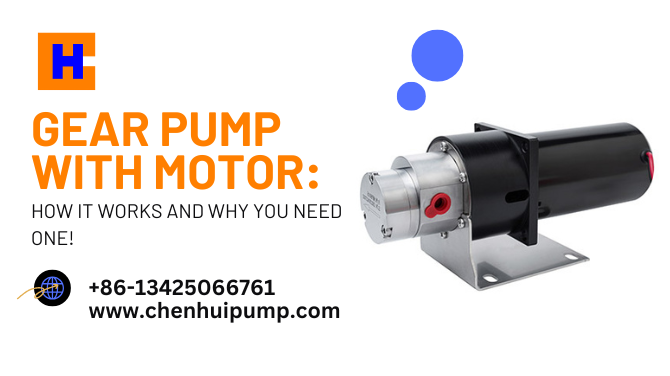
In industrial operations, efficient fluid transfer is critical for ensuring seamless production processes. Whether it’s in the chemical, food, oil, or pharmaceutical industries, the need for reliable and high-performing pumping systems has never been greater. One such solution that has transformed fluid transfer applications is the Gear Pump With Motor.
A Gear Pump With Motor combines two crucial components — a gear pump and an electric motor — to ensure high efficiency, consistent flow rate, and minimal maintenance. This integrated system is widely used in various industries for pumping oil, chemicals, beverages, and other viscous fluids.
What Is a Gear Pump With Motor?
A Gear Pump With Motor is a type of positive displacement pump that utilizes gears to transfer fluids. It is powered by an electric motor that drives the gears, allowing the liquid to be moved from one point to another. This combination of motor and gear pump ensures smooth, continuous fluid transfer with minimal pulsation.
The motor is responsible for providing the mechanical energy required to rotate the gears inside the pump. The gears then create a vacuum at the pump inlet, allowing fluid to enter and be pushed out through the outlet.
Key Components of a Gear Pump With Motor
To understand the efficiency of a Gear Pump With Motor, it’s important to know its key components:
- Motor: Provides the mechanical energy to drive the gears.
- Driving Gear: Connected to the motor and rotates to engage the second gear.
- Driven Gear: Moves in synchronization with the driving gear to facilitate fluid transfer.
- Pump Casing: Houses the gears and ensures fluid containment.
- Inlet/Outlet Ports: Allows fluid to enter and exit the pump.
Working Principle of a Gear Pump With Motor
The working mechanism of a Gear Pump With Motor is relatively simple but highly efficient:
- When the motor is powered, it rotates the driving gear.
- The driving gear, in turn, engages the driven gear, creating a vacuum at the pump’s inlet.
- This vacuum allows the fluid to enter the pump.
- As the gears continue to rotate, the liquid is trapped between the gear teeth and the pump casing.
- Finally, the liquid is pushed out through the outlet port.
The seamless coordination between the motor and the gears ensures a continuous and smooth fluid transfer process.
Types of Gear Pumps With Motors
Depending on the design and application, there are three main types of Gear Pumps With Motors:
1. External Gear Pump With Motor
In an external gear pump, two separate gears rotate in opposite directions. One gear is driven by the motor, and the second gear is driven by the first gear. This type of gear pump is ideal for transferring low to medium-viscosity fluids like oils, solvents, and fuel.
2. Internal Gear Pump With Motor
In an internal gear pump, one larger outer gear rotates around a smaller inner gear. This design offers higher efficiency in transferring high-viscosity fluids such as honey, molasses, and lubricants.
3. Helical Gear Pump With Motor
A helical gear pump utilizes helical gears, which are designed to reduce noise and vibration during operation. This type of gear pump is widely used in precision industries where minimal pulsation and noise are required.
Benefits of Using a Gear Pump With Motor
Investing in a Gear Pump With Motor offers numerous advantages for industrial applications. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. High Efficiency and Consistent Flow Rate
A Gear Pump With Motor provides a steady and consistent flow rate, ensuring continuous fluid transfer. Unlike centrifugal pumps, gear pumps do not experience flow fluctuations, making them ideal for industrial applications.
2. Compact Design and Easy Installation
Another significant advantage of Gear Pumps With Motors is their compact and space-saving design. They can be easily installed in industrial setups without requiring excessive space.
3. Minimal Maintenance Requirements
Since gear pumps have fewer moving parts, they require very little maintenance. This reduces downtime and increases the overall productivity of industrial operations.
4. Suitable for Handling Viscous Fluids
Gear Pumps With Motors are particularly efficient in transferring viscous fluids such as oils, syrups, adhesives, and lubricants. The gears create a powerful suction force that ensures smooth transfer without causing any blockages.
5. High Durability and Long Service Life
The materials used in Gear Pumps With Motors, such as stainless steel, cast iron, or composite plastics, offer excellent durability. This ensures a long service life, minimizing replacement costs.
Applications of Gear Pumps With Motors
The versatility of Gear Pumps With Motors makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Here are some of the most common uses:
1. Chemical Processing Industry
In the chemical industry, transferring hazardous and corrosive chemicals requires high-precision pumps. Gear Pumps With Motors provide leak-free operation, ensuring safe and efficient chemical transfer.
2. Oil and Lubricant Transfer
In the oil and lubricant industry, maintaining a continuous flow of oil is essential. Gear Pumps With Motors efficiently transfer high-viscosity oils, lubricants, and grease without any disruption.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
Food-grade gear pumps are widely used in the food and beverage industry for transferring syrups, sauces, oils, and other liquid ingredients. Their leak-free design ensures contamination-free fluid transfer.
4. Hydraulic Systems
In hydraulic power systems, Gear Pumps With Motors play a crucial role in providing consistent hydraulic fluid transfer. This allows hydraulic machinery to operate smoothly without interruptions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gear Pump With Motor
Before purchasing a Gear Pump With Motor, consider the following factors:
1. Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements
Determine the required flow rate (liters per minute) and pressure (bar or PSI) for your specific application. This will help you select the appropriate gear pump size.
2. Fluid Type and Viscosity
Consider the viscosity of the fluid you intend to transfer. High-viscosity fluids may require specialized gear pumps with higher torque motors.
3. Material Compatibility
Ensure that the pump material is compatible with the fluid being transferred. For example:
- Stainless steel for corrosive chemicals.
- Cast iron for heavy oils and lubricants.
- Plastic for non-corrosive liquids.
4. Temperature Range
Verify if the Gear Pump With Motor can handle high-temperature or low-temperature fluids based on your application.
Why Buy from Zhuhai Chenhui Technology Co., LTD?
When it comes to reliable, high-quality Gear Pumps With Motors, Zhuhai Chenhui Technology Co., LTD is the leading manufacturer in the industry. Here’s why you should consider them:
✅ High-Quality Manufacturing
The company uses advanced engineering technology to manufacture premium-quality Gear Pumps With Motors that guarantee superior performance.
✅ Customization Options
Whether you need a standard or customized Gear Pump With Motor, Zhuhai Chenhui Technology Co., LTD offers custom solutions tailored to your application.
✅ Affordable Pricing
They offer competitive pricing without compromising product quality, ensuring that businesses get the best value for their investment.
✅ Excellent Customer Support
With dedicated customer support, Zhuhai Chenhui Technology Co., LTD ensures quick response and effective technical assistance.
A Gear Pump With Motor is an indispensable component in various industrial operations, offering high efficiency, smooth fluid transfer, and minimal maintenance. Investing in a high-quality gear pump can significantly improve productivity, reduce operational costs, and ensure long-lasting performance.
If you’re looking for a reliable supplier, Zhuhai Chenhui Technology Co., LTD offers the best-in-class Gear Pumps With Motors that guarantee superior performance and longevity.
FAQs
Q1: What is the lifespan of a Gear Pump With Motor?
The average lifespan is 10-15 years, depending on maintenance and operating conditions.
Q2: Can Gear Pumps handle high-viscosity fluids?
Yes, gear pumps are ideal for transferring high-viscosity fluids like oil, lubricants, and syrups.
